Understanding the Challenges of Wine Cellar Cooling in Dry Climates
Wine enthusiasts and collectors understand the importance of proper wine storage conditions, as temperature and humidity play a significant role in preserving the quality and aging potential of wines. However, in dry climates, where the ambient air lacks moisture, maintaining optimal conditions in a wine cellar becomes challenging. In this blog post, we will delve into the specific challenges of wine cellar cooling in dry climates and explore effective strategies to overcome them, ensuring that your wine collection remains in excellent condition.
- Low Humidity Levels: One of the primary challenges in dry climates is the lack of humidity. Low humidity levels can lead to excessive evaporation from wine bottles and corks, causing premature oxidation and potentially affecting the overall quality of the wine. To mitigate this challenge, it is crucial to implement humidity control measures in your wine cellar. Consider using a humidification system or incorporating natural humidity sources such as water features or moisture-retaining materials.
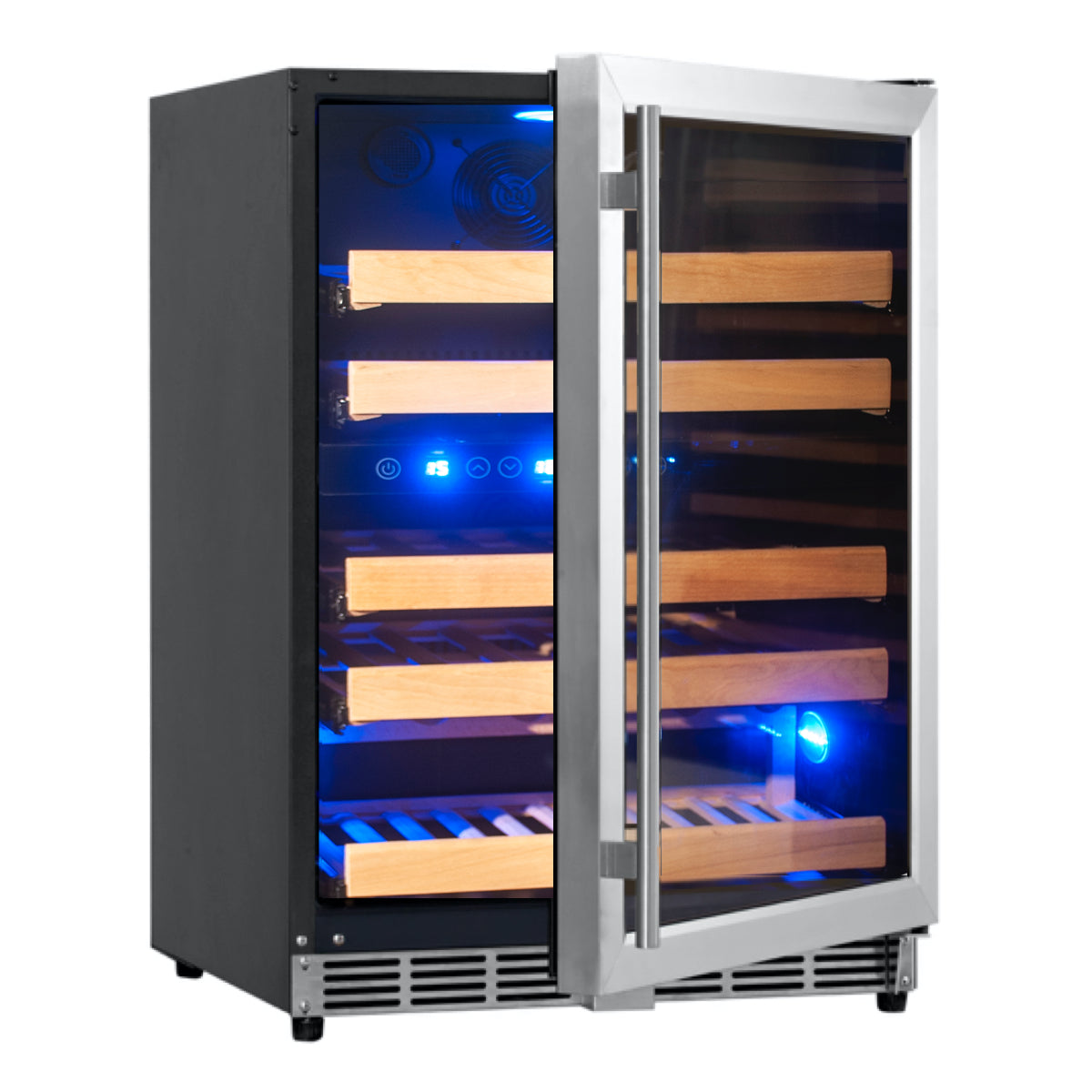
- Temperature Fluctuations: Dry climates often experience significant temperature fluctuations between day and night or across different seasons. These fluctuations can be detrimental to wine storage, as constant temperature changes can impact the wine's aging process and lead to flavor degradation. Investing in a reliable wine cellar cooling system that can maintain a consistent temperature is essential. Look for cooling systems with precise temperature control and insulation features to combat the challenges posed by fluctuating temperatures.
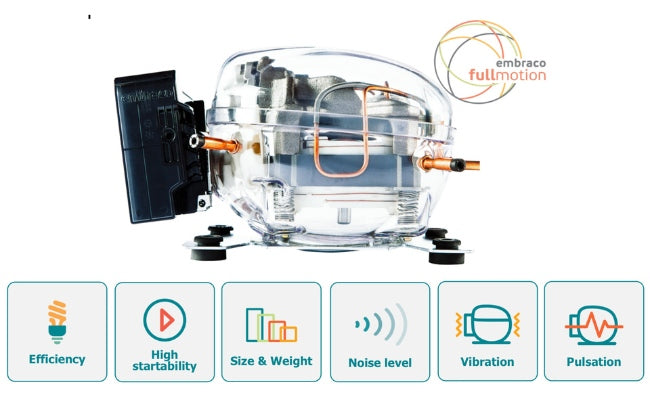
- Energy Efficiency: In dry climates, where cooling is required for an extended period, energy efficiency becomes a critical consideration. The hot and arid conditions can strain cooling systems, leading to increased energy consumption. Opt for energy-efficient cooling units that are specifically designed to handle the demands of dry climates. Additionally, ensure that your wine cellar is well-insulated to minimize energy loss and reduce the workload on the cooling system.
- Air Quality and Ventilation: Dry climates often have dusty and dry air, which can affect the air quality within a wine cellar. Dust particles can settle on wine bottles and compromise the overall cleanliness and integrity of the collection. Proper ventilation and air filtration systems are essential to maintain clean air and minimize dust accumulation. Regular cleaning and dusting of wine bottles and cellar surfaces are also recommended to preserve wine quality.
- Monitoring and Maintenance: Regular monitoring and maintenance are crucial in dry climates to ensure that the wine cellar cooling system is functioning optimally. Keep a close eye on temperature and humidity levels using a digital thermometer and hygrometer. Regularly check the cooling system for any signs of wear or malfunction and schedule professional maintenance as needed. By staying proactive, you can address any issues promptly and maintain ideal conditions for your wine collection.
Tips for Proper Wine Cellar Cooling in Arid Regions
Proper wine cellar cooling is crucial for preserving the quality and longevity of your wine collection. In arid regions, where dry and hot conditions prevail, maintaining optimal temperature and humidity levels becomes even more challenging. Let’s talk about essential tips to ensure proper wine cellar cooling in arid regions, allowing you to protect your wines and enhance their aging potential.
Invest in a Reliable Cooling System
Selecting the right cooling system is the foundation of proper wine cellar cooling. Opt for a cooling unit specifically designed for arid regions, capable of handling high ambient temperatures. Look for systems with precise temperature control and humidity management features to ensure a consistent and stable environment for your wines.
Insulate Your Wine Cellar
Effective insulation is key to maintaining desired temperature and humidity levels. Insulate your wine cellar properly to minimize temperature fluctuations and reduce the workload on the cooling system. Use insulation materials such as foam insulation, vapor barriers, and weatherstripping to create a well-sealed environment that minimizes heat transfer.
Monitor and Control Humidity Level
Arid regions are known for their low humidity levels, which can negatively impact wine storage. Install a humidification system in your wine cellar to maintain optimal humidity levels (around 55-75%) for proper cork moisture and wine aging. Monitor humidity using a hygrometer and adjust the humidification system as needed to prevent excessive drying of corks and evaporation from wine bottles.
Consider Passive Cooling Methods
In addition to an active cooling system, you can employ passive cooling methods to help maintain optimal temperatures in your wine cellar. Utilize underground or cellar location if available, as the naturally cooler and more stable temperatures can help offset the heat from arid climates. Incorporate natural ventilation techniques, such as vents, fans, or air circulation systems, to promote air movement and regulate temperature.
Shield Your Wine Cellar from Direct Sunlight
Direct sunlight can cause temperature spikes and UV damage to your wines. Protect your wine cellar by installing light-blocking curtains or shades on windows or using UV-resistant glass for windows and doors. Consider tinting windows or using reflective films to minimize heat transfer from sunlight.
Regularly Maintain and Service Your Cooling System
To ensure optimal performance, schedule regular maintenance for your wine cellar cooling system. Clean or replace air filters, inspect and clean condenser coils, and check refrigerant levels as recommended by the manufacturer. Regular maintenance will improve energy efficiency, prolong the lifespan of your cooling system, and help maintain consistent cooling in your wine cellar.
Keep the Wine Cellar Well-Sealed
Prevent outside air from infiltrating your wine cellar by ensuring it is well-sealed. Check for any gaps or leaks in windows, doors, or walls and seal them appropriately. This will help maintain a controlled environment and prevent outside heat and humidity from affecting your wines.
The Effects of Dry Climates on Wine Storage: Risks and Solutions
Risk 1: Excessive Evaporation
Dry climates are characterized by low humidity levels, which can lead to excessive evaporation from wine bottles. When the surrounding air lacks moisture, corks dry out, allowing air to seep into the bottle and accelerate oxidation. This can result in premature aging, loss of flavors, and compromised quality.
Solution:
Maintain optimal humidity levels within your wine storage area. Invest in a reliable humidification system specifically designed for wine cellars. This system will introduce moisture into the air, preventing excessive evaporation and keeping the corks moist. Aim for humidity levels between 55% and 75% to ensure the longevity of your wines.
Risk 2: Temperature Fluctuations
Dry climates often experience significant temperature fluctuations, with hot days and cooler nights. These fluctuations can be detrimental to wine storage, as constant changes in temperature can impact the aging process and compromise the delicate balance of flavors and aromas.
Solution:
Invest in a high-quality wine cellar cooling system capable of maintaining a consistent and controlled temperature. Ensure that the cooling unit is equipped with precision temperature control to offset external temperature fluctuations. Regularly monitor and adjust the temperature settings as needed to create a stable environment for your wines.
Risk 3: Increased Oxidation
In dry climates, the lack of humidity and higher temperatures can accelerate the oxidation process in wines. Oxidation can lead to flavor deterioration, loss of aromas, and a decrease in overall quality. It is essential to protect your wines from excessive exposure to oxygen.
Solution:
Minimize the contact between wine and air by properly sealing wine bottles. Ensure that corks are in good condition and securely inserted into the bottles. Consider using alternative closure systems such as screw caps or synthetic corks, which provide a tighter seal and reduce the risk of oxidation. Regularly inspect your wine collection and replace any compromised or damaged closures.
Risk 4: Heat Damage
Dry climates often bring scorching temperatures, which can have a detrimental effect on wine quality. High temperatures can accelerate chemical reactions within the wine, leading to premature aging and the development of off-flavors.
Solution:
Store your wine in a cool, dark environment away from direct sunlight and heat sources. Invest in a well-insulated wine storage area or cellar that can shield your wines from extreme temperatures. Consider using reflective window films, light-blocking curtains, or UV-resistant glass to prevent heat transfer and protect your wines from harmful UV rays.
Risk 5: Increased Energy Consumption
In arid regions, where cooling is required for extended periods, energy consumption can be a concern. The continuous operation of cooling systems to combat high temperatures and maintain ideal wine storage conditions can lead to increased energy usage.
Solution:
Opt for energy-efficient cooling systems designed for wine cellars. Look for units with high energy efficiency ratings and advanced temperature control features. Properly insulate your wine storage area to reduce energy loss and minimize the workload on the cooling system. Regularly maintain and clean your cooling system to ensure optimal performance and energy efficiency.